Let’s be real here, nobody is 100% certain what all of the SEO ranking factors are these days. However, most will agree that a handful of factors definitely contribute to how your content ranks. SEO requirements constantly evolve and it is a serious task to stay on top of the most recent developments. That being said, in order to rank high on Google, you need to be in the know.
Another accepted truth is that well-optimized sites earn more and more traffic over time. If you’re new to the SEO game, more traffic typically means more leads, which, in turn, leads to more sales. Without SEO, searchers cannot find your site and all the sweat and tears that you put into your site will be for nothing. In this post, we’re going to discuss what SEO is at its core and touch on a handful of essential SEO ranking factors that will help you dominate the SERPs.

Understanding SEO (aka “How Do I Rank Higher on Google?”)
Many wonder how Google ranks content. This is a very complicated (and potentially loaded) question, so let’s start by answering a few simpler questions about SEO.
What is “Ranking” in SEO?
As you likely already know, SEO stands for search engine optimization, which involves improving web pages so they are more likely to rank high on the search engines. Let’s be real here, by search engines I really mean Google…does anyone really use any other search engines?
So…how does that work exactly? Let’s dive in and explore a bit deeper.
In the world of SEO, ranking refers to your content’s position on the SERPs. Ranking #1 means that when people search for a particular term, your content is the first result…after promoted results, featured snippets, and answer boxes.
Appearing in the top 3 results is excellent because your click-through rates increase exponentially the closer you get to the #1 spot. The graphic below from Backlinko provides a clear and accurate illustration of the relationship between SERP ranking and click-through rate.

If your content isn’t ranking in the top 3 spots, don’t freak out. Appearing on the first page at all (top 10 spots) is definitely worth writing home about. Why? Well, 95% of people never explore the SERPs beyond the first page.
What Does Google Look for in SEO?
Google’s ultimate goal is to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” Thus, delivering relevant content via its search engine is a huge part of that. Here’s an extremely simplified outline of how it all works:
- Google’s bots (aka “spiders”) crawl the web by visiting web pages.
- Upon visiting a page, Google’s bots add optimized pages to its index and then catalogs them.
- Finally, when people search for a given term or phrase, Google presents the best results based on the query.
Google employs a series of complex and intricate algorithms to determine which content to show on its SERPs and in which order. We’ll dive into this more later on.
Once your content lands on the SERPs, you have to rely on your page titles and meta descriptions to encourage searchers to click on your content and visit your site.
How Do Google Search Rankings Work?
When people want to find information, they type (or say) words related to what they seek. These words are called keywords – we’ll explore keywords more in the content optimization portion of this guide.
Maintaining a high ranking on Google isn’t just about making the most of competitive keywords. It’s also about the quality of the information you share.
According to Google’s search quality ratings, when it indexes the main content of each page, it looks for factors such as:
- Purpose of the page
- Content quality (and amount)
- Website info & info about the creator
- Website & content creator reputation
- User interaction on the page (time on page, bounce rates, etc.)
- Expertise, authority & trustworthiness (E-A-T)
Based on the rating guidelines outlined above, Google shows searchers the most relevant, high-quality content related to their query. As you may have guessed, the most relevant content shows first.
One of the primary goals of addressing SEO ranking factors is to let Google know what your content is relevant to a particular query.
Before we dive into the two types of SEO, let’s discuss the concept of expertise, authority & trustworthiness (E-A-T) in more detail.

What is E-A-T & Why Does It Matter
Way back in the day (August 2018 to be exact), Google implemented the “medic update,” which placed a lot of value on expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (E-A-T) as core ranking factors. Google even went so far as to change some instances of “high-quality content” to “high EAT.”
The primary objective of this development was to ensure that users weren’t just getting the highest quality content, but also getting the right information. This is super important to understand.
Google realized that most searchers use the Google platform for just about everything. This means that Googlers’ lives could be seriously impacted for the worse if the wrong results appear.
Websites that could lead to potentially life-changing results fall under the “your money or your life” (YMYL) umbrella. Think about medical sites, financial planning sites, or anything that could change the status of someone’s happiness, health, or wealth.
When someone goes to Google for information that could have real-world implications, Google wants to ensure that it’s giving its users the most accurate information possible.
This means that you not only need to produce quality content, but you also need to monitor your site’s reputation as well.
Instead of focusing exclusively on what a site’s page says, Google now tries to understand who is saying it. This is especially true for YMYL sites.
This wrinkle means that you need to look at each category individually:
- Expertise: Does the author have the necessary skills and knowledge in their field?
- Authority: Is this the best possible resource to answer the searcher’s question, or is there another option that would be a better source?
- Trustworthiness: Does the author provide an honest and unbiased presentation of the topic they cover?
You’re now likely wondering how exactly Google measures E-A-T – this is tricky, to say the least.
Nobody Outside of Google Really Knows
We may not know the exact rhyme and/or reason. However, we do know that Google has a massive team of human searchers to ensure that E-A-T is measured as accurately as possible. As Ahrefs explains, Google measures E-A-T in three steps:
- Engineers create an algorithm to improve and enhance search results.
- Quality Raters (humans searchers) see search results with and without the alterations made by the engineers.
- Google takes feedback from the Quality Raters and decides whether or not to use the algorithm change moving forward.
This system is anything but perfect. However, it is rather effective at measuring a site’s expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
Some SEO professionals downplay the importance of E-A-T as a ranking factor. This may sound absurd given everything we just discussed, but there’s really no rebuttal since nobody really understands Google’s complex ranking algorithm.
That being said, a handful of reputable SEO gurus have documented strong correlations between E-A-T and ranking.
SEO wizard Marie Haynes, CEO of Marie Haynes Consulting (MHC), provides some insight on how E-A-T impacts rankings:
“The team at MHC has seen quite a few websites that we believe have been negatively affected by Google Quality updates because they have a lack of E-A-T. We have also had the joy of helping businesses to improve their Google E-A-T with resulting traffic increases.” – Marie Haynes
How to Increase Your E-A-T
So…what does this mean for you? More importantly, how can you increase your E-A-T? Well, here are a few tips:
- Develop an in-depth “About Us” page on your site
- Optimize your page for searcher intent (we’ll dive into this topic later)
- Proudly display any awards, certificates, or credentials on your site
- Increase your authority across the web with guest posts
- Respond to both positive & negative reviews
- Ensure that information on your site is unbiased and as accurate as possible
- Provide easy access to a contact page with numerous ways for users to reach your team
These are some of the top ways you can increase your E-A-T and improve your rankings. When all is said and done, a lot of it comes down to using best practices to manage your online reputation.
I want to make this painfully clear so that even those of you in the back get the message. There’s never a guarantee of a page one or #1 rank. This is especially true since SEO guidelines are constantly changing, which, in turn, means that search engine rankings are also changing.
Next, we’re going to tango with a coup9le of SEO terms you’ve likely heard on a regular basis.
What are On-Page and Off-Page SEO?
On-page and off-page SEO are two terms you’ll hear a lot when discussing SEO ranking factors.
On-page SEO consists of the factors on your website that you can optimize, such as the internal code and general content.
Off-page SEO involves the actions that take place outside of your site that impact your site’s trustworthiness and authority. The primary factors that drive off-page SEO are inbound links and social signals.
Both on-page and off-page SEO are among the top SEO ranking factors.
Before we kick things into gear and dive into our top 10 ranking factors, let’s confirm that we’re on the same page about monitoring and tracking ranking.
Monitoring Search Engine Rankings

Before you can even think about improving your SEO ranking, you need to know where you currently stand.
There are a number of ways you can do this. First, you could search Google using the terms that you believe customers will use to find you. Make sure you use an incognito browser to ensure that the results aren’t skewed by Google’s personalization.
This method may work just fine for smaller sites, but the same doesn’t ring true for larger sites with hundreds of pages. If you’re monitoring the SERP rankings for a larger site, you’ll want to enlist the assistance of a tool of some sort.
My personal favorite is Neil Patel’s UberSuggest. All you need to do is enter your domain and UberSuggest will take it from there.

Top 10 Current Ranking Factors for Google
1.) A Secure and Accessible Website
This shouldn’t come as a surprise, but the first ranking factor on this list has to do with having the right kind of URL. More specifically, you want a URL that Google’s bots can easily reach and crawl.
In simpler terms, Google has to be able to visit the URL and look at the content to understand what the page is about. You can help Google’s bots out by providing the following:
- A well-coded website
- A robots.txt file that tells Google where it can and can’t look for your site information
- A sitemap that lists all of your pages
If you’re operating a WordPress site, you can set up a sitemap with Yoast.
HTTP isn’t a factor in deciding whether or not to index a page, but Google’s own John Mueller has tweeted that it’s a “light-weight ranking factor” and that “having HTTPS is great for users.” Most digital marketers will agree.
If you haven’t invested in an SSL certificate yet, you really should.
2.) Page Speed (Especially Mobile Page Speed)
Page speed has been a major SEO ranking factor for years. Why? Simple. Google wants to improve users’ experience on the web and fast-loading web pages will do just that.
Google unleashed a search engine algorithm update that focused on mobile page speed back in July 2018. It is worth noting that if your site fails to load quickly on mobile devices, Google may very well penalize it.
You can use Google’s mobile testing tool to see how your site stacks up in terms of mobile metrics.

Again, if you’re using WordPress, our friends over at WPBeginner offer a series of tips on how to speed up your WordPress website.
Naturally, the best place to start is Google Search Console since it has an entire section dedicated to updating you on your site’s performance.
3.) Mobile Friendliness is a Critical SEO Ranking Factor
While we’re on the topic of mobile, mobile-friendliness is another huge SEO ranking factor. More people use mobile devices today than desktops to access the web. This is one of the key reasons why Google has changed how it ranks search results.
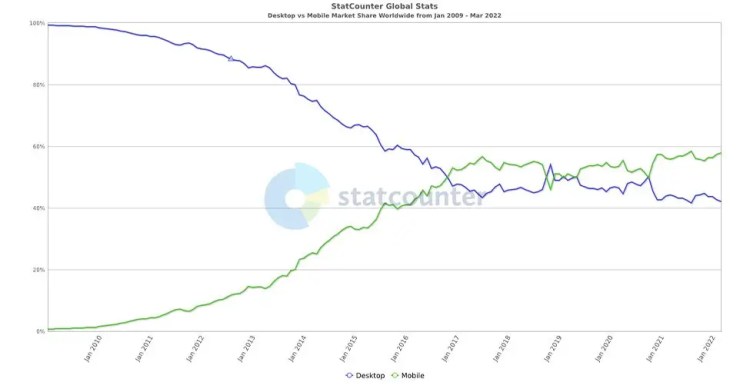
As you can see in the chart above, most users surfed the web via desktop browsers until late-2016 when mobile browsers all but took over from that point forward. Granted, there are a few hiccups where users preferred surfing on their desktop over their mobile devices, but mobile devices have reigned supreme for the most part since 2017.
Google’s mobile-first index is now very real, which means it’s drawing its results from mobile-optimized sites first, rather than sites geared towards desktops. if your site isn’t mobile-optimized, you run the risk of paying for it on the SERPs.
Many of the SEO ranking factors that we’ll review in this article will help you lay the foundation for a good search engine ranking, but you also need to be mindful of user experience once people land on your site.
You want to constantly ask yourself the following questions:
- Do I have a responsive site that automatically resizes to fit any and all devices?
- Is it easy to read my fonts on a small screen?
- Are my menus accessible and easy to navigate?
- Do I ensure that essential content isn’t hidden by ads?
You can find more tips on mobile-friendly design to improve your rankings on Google in this awesome mobile conversion rate guide from OptInMonster.
Google AMP
If you have a solid team, enough time, and a surplus of energy, you may consider exploring Google AMP (accelerated mobile pages). The upside if you adopt AMP is that your pages load in an instant on mobile devices. There have also been rumors that Google ranks sites built with AMP higher than those that are not built with AMP.
The downside to AMP is that you’ll need to make a second version of your site that follows AMP’s guidelines. Furthermore, you’ll also need to maintain everything. As you can imagine, this can become quite time-intensive.
Regardless of whether you pursue the AMP route or not, you need to be sure that your site is 100% optimized for mobile devices.
4.) Domain Age, URL & Authority

Fun Fact: Nearly 60% of sites that rank in Google’s top ten are three years old or older.
Data from an Ahrefs study of 2+ million pages suggests that few sites less than a year old earn a spot in Google’s top 10.
That being said, if you’ve had a site for a while and have optimized it using the tips in this article, you’re at a clear advantage.
In some cases, the domain name matters. Though Google has penalized exact-match domains – those where the target keyword is in the URL – that penalty is generally for spammy sites with thin content.
Research from Moz shows that exact-match domains that are deemed to be relevant, valuable, and high-quality can see a ranking boost because of it. However, if your website is already established, you don’t need to go hunting for an exact-match domain for your business.
So…what’s the best route for choosing your domain? Simple. Focus on a URL that reflects your business and optimize the living daylights out of it.
When it comes to search engine ranking factors, authority matters. As you’ll find out, that’s usually a combination of superb content and off-page SEO signals. Furthermore, thanks to E-A-T, it can also include the authority of the content’s creator.
Moz has codified this into page authority and domain authority scores, both of which rank from 0 to 100 and tell you how likely a specific page or domain is to rank in the SERPs.
You can check your domain authority or page authority with Moz’s Domain Analysis SEO Tool. All you need to do is plug in a URL and it’ll spit out a report showing domain authority, page authority, established links, and new links.
5.) Optimized Content is a Massive SEO Ranking Factor

We’ve talked a lot about content in this guide to Google SEO ranking factors so far. Why? Well, content is one of the most important search ranking factors.
With that in mind, let’s dig deep and discuss what optimizing content for SEO really means.
Google’s search algorithm relies heavily on keywords. These are words and phrases that searchers use when they’re looking for information online. They’re also the words and phrases that describe the topics your site is about.
These terms will match up in a perfect world. This is why it’s critical that you sprinkle in keywords throughout your content.
One negative SEO ranking factor that you need to be mindful of is duplicate content. When it comes to SEO, fresh content always reigns supreme. If you do have similar content, make sure to tell Google which one should be ranked as more authoritative by employing canonical URLs.
One of the biggest questions most novice SEO professionals have pertains to how best to use Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords to optimize content. So, let’s dive into the world of LSI keywords.
Understanding LSI Keywords and SEO Ranking
SEO isn’t all about the primary keyword. It’s also important to include terms related to the main terms people are searching for. These terms are called latent semantic indexing keywords. They provide an online word association to help Google know which results to serve.
For instance, using the correct LSI keywords will inform Google that when searchers type in “mini,” your page is relevant to the car, not the skirt, and vice versa.
It’s definitely worth noting that as more people search by voice, content optimization includes optimizing for questions and natural language searches. This means that some LSI keywords will be longer since people typically speak differently than they type.
Let’s unpack that a bit more. Let’s say you own a restaurant and half of your customers type the phrase “best restaurant near me.” But then people also search for “what’s the best restaurant in Detroit” when searching by voice. Even though both questions target the same thing, Google’s results may present differently. Using LSI keywords would be one way to ensure that your restaurant ranks for both question phrases. The more you help Google understand your content, the more likely you are to rank in your niche.
Now let’s quickly touch on keyword stuffing. This blackhat SEO tactic is straight-up outlawed because it results in low-quality web pages and will ultimately hurt your SEO ranking.
So the lesson here is that you only want to include your keywords in a way that is organic and sounds natural.
Understanding Search Intent for Content Optimization

Search intent is also an important SEO ranking factor when it comes to optimizing your content. Search intent entails understanding what people are really looking for when they submit a query.
Let’s say you’ve identified “Michigan real estate” as a keyword you wish to rank for. You may think that writing content for people on the hunt for real estate in Michigan is a good idea. However, if the people searching for said phrase also include realtors looking to sell properties in Michigan, then your content will not meet their needs. This, in turn, means that your content will not rank.
Through a sequence of low click-through rates and high bounce rates, Google will quickly realize that your content doesn’t align with the user’s search intent.
Sometimes, it’s easy to figure out what people are looking for. For instance, if they use the term “compare,” they’ve likely created a shortlist of options and want to make sure they choose the best possible option. If they include the word “buy,” then they’re likely looking to purchase a product.
The keywords will change depending on whether they want to:
- Find a particular website (navigational)
- Get the answer to a question (informational)
- Research information before making a purchase (investigational)
- Make a purchase (transactional)
Well-optimized business sites will feature content for each of those search types.
So, how do you ensure your keyword aligns with user intent? Simple – go directly to the source!
Open a Google search in your private browser and type in your keyword. You then want to see which results are currently ranking and determine if your content would be a good fit. If not, you need to restart your keyword research. This is also a great time to dig a little deeper and see why certain pages are ranking.
You can also do a competitive analysis of the top 10 results in the SERP to see how you can improve your content. Upon running a competitive analysis, you can then fully optimize your content and provide even more value than what the current top search results provide.
Is Content Length an SEO Ranking Factor?
Yes! Google wants high-quality content that has some substance to it. Writing more words just to increase the length of a post isn’t the best course of action. However, if a topic requires a deep dive, then you best give it the attention it deserves.
Recent research suggests that content in excess of 2,000 words gets more top ten rankings in Google search results than content that falls short of 2,000 words.
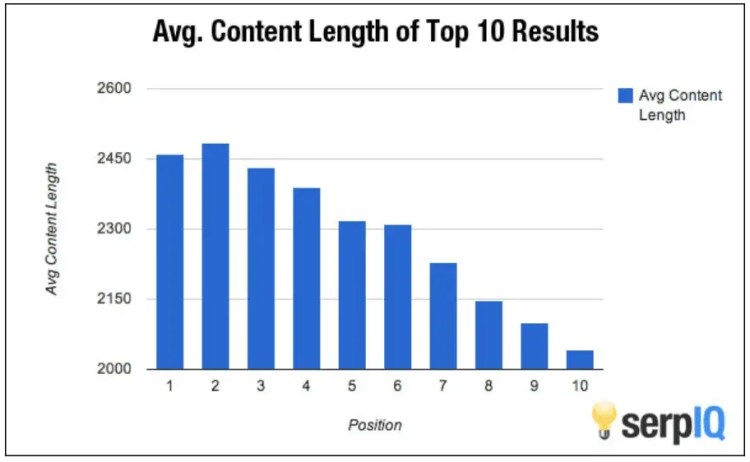
This word count isn’t set in stone and there are most definitely a handful of exceptions. However, you should strive to produce content that exceeds the 2,000-word target if you want an honest shot at the top spot for the keywords of your choosing.
Longer content also attracts more links and shares, which are two other important ranking signals that we’ll cover in just a bit.
SEO Ranking Factors: Answer Boxes or the “Zero Position”
Google has shown a lot of interest in delivering answers via answer boxes, so that’s another aspect you need to consider when optimizing your content.
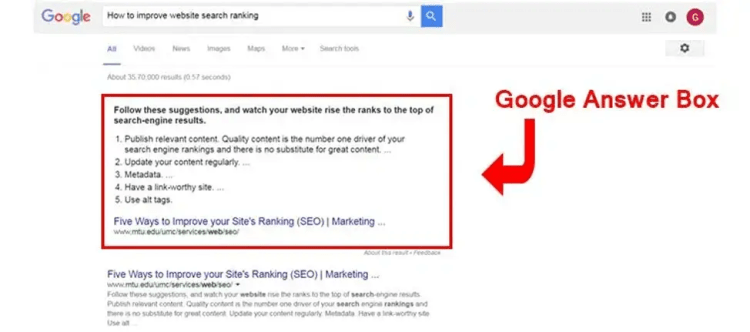
Experience suggests that optimizing for answer boxes means:
- Answering questions
- Including the questions as headings with properly formatted title tags
- Ensuring that the answers are correct, relevant, and brief
- Targeting content to keywords that already have answer boxes
- Including lists and/or tables
While earning the first spot as an answer box in the coveted “zero position” is great, there is one major you need to consider:
It sometimes hinders people from clicking through to your site.
Since people get the answer to their question right away, they may have no reason to click through to your website. This means you may have 100,000 see your snippet in the answer box, but only 5,000 actually click through to your article.
Let’s be real though, getting that zero position straight up rocks because it means Google thinks highly of your content. Furthermore, you’ll get a ton of brand recognition and you’ll also likely end up with more traffic than you would have without earning the zero position.
Using Video to Improve SEO Ranking
Here are a few statistics that support the inclusion of video to improve your SEO ranking…
- Viewers retain 95% of a message when they watch it in a video, versus 10% when reading it in text form
- Marketers who use video grow revenue 49% faster than non-video users
- 96% of people have watched an explainer video to learn more about a product or service
- One-third of all online activity is spent watching videos
So…what does this mean? It means that you should definitely start including videos as part of your content strategy. Video gets read, shared, and linked to, which provides plenty of signals to increase your search ranking.
6.) Technical SEO
We touched on it earlier, but we’ll say it again. Getting the code right is one aspect of optimizing content for better search engine rankings. This can be terrifying for some, especially if you’re more of a wordsmith and less of a tech wizard.
Here are some of the aspects you can control even if you don’t speak code:
- Add keyword phrases in page titles. This is where Google looks first to determine which content is relevant to a user’s query
- Use header tags to show content hierarchy starting with your title at H1 and then use H2 or H3 for subheaders
- Create a meta description that not only entices readers but also includes your keyword phrase
- Keep your meta descriptions short and snappy – 160 characters is a good target
- Include keyword phrases in image alt tags to show how those images are relevant to the core content
- Including alt tags also helps people who are visually impaired
- Use schema markup to tell Google what kind of content you’re producing
You can easily accomplish all of this with my all-time favorite SEO tool – Yoast!
7.) User Experience (RankBrain)

Google has been using artificial intelligence (AI) to more effectively rank web pages for a while now. The AI entity that Google uses is called RankBrain. RankBrain takes a number of signals into account that impacts your search engine ranking. A few of these signals include:
- Click-Through Rate: the percentage of people who click to visit your site after an entry shows in the search results
- Bounce Rate: the number of people who click on your page and quickly return to the search results
- Dwell Time: the time visitors spend on your site after they’ve arrived
If people land on your site, don’t like it and bounce away, then Google will think it’s not relevant to their needs. If enough people do this, then you might find it more difficult to rank high in the search results.
This is likely a strong indicator that your content doesn’t align with the searcher’s intent. You may need to go back and target more effective and meaningful keywords.
On the other hand, if people click through to your site and stick around for a decent chunk of time, Google will recognize that your content is relevant to their search.
So, when you optimize titles, descriptions, and content to get clicks and deliver value on the other end, you will likely boost your search engine rankings.
8.) Links
As I stated earlier in this article, the web is built on a heaping mound of links. So, it should go without saying that links are a crucial SEO ranking signal. There are three primary kinds of links that you need to keep in mind:
- Inbound links
- Outbound links
- Internal links
All three are usually tied to a descriptive anchor text.
Inbound Links
Google uses inbound links as a way to determine how authoritative and relevant your content is.
The best-case scenario is where an authoritative site includes a relevant link to your site in its content. So, if the Content Marketing Institute includes a link to your post on content marketing, that’ll be perceived better than if a random person with a janky website links to it.
Odds are you’ve likely heard of inbound links referred to as “backlinks.” Your goal is to get as many highly authoritative sites to link back to your site. This also means you want to have as few inbound links from sketchy sites too.
You can keep tabs on your inbound links with a tool like SEMrush or one of the keyword research tools I mentioned earlier in this post.
Outbound Links
At the same time, you want to show that you’re generating high-quality content for your visitors. This involves using outbound links by linking to relevant and authoritative sites in your niche.
So does this mean that you should just have tons of outbound links to boost your authority? NO.
All this means is that you’re conducting ample research. You should only pull from reliable sources with high domain authority. In all honesty, for the sake of your audience, you should probably be doing this anyway to ensure you provide as much value as possible.
Internal Links
Lastly, linking to your own content can help tie pages together for both Google and your audience. If you have an authoritative page and link to another page on your site, doing so helps your visitors find the other page and also passes on some authority. This helps the second page rise in the search engine rankings.
As you generate your content, make sure to build a sturdy web of internal links so your pages can support each other. Also, remember what I said at the start of this section:
All three types of links are tied to descriptive anchor text. When you add a link to a piece of text in your content, the text should clearly describe where the link is going.
9.) Social Signals

When people share your content on social networks, this is another sign that it’s of great value. Cognitive SEO’s study of 23 million shares found a clear link between social shares and search engine rankings.
However, Google officially stated that social shares are not a direct ranking factor. Links from Twitter and Facebook are not counted the same as links from authoritative websites.
Naturally, there’s no getting around the clear correlation between social shares and search engine ranking. Mind you, correlation does not equate to causation. However, this is likely due to a number of related factors:
- More social shares generate more traffic to the pages to which they’re linked
- More shares also make your content more likely to form backlinks
Between these two factors, getting more social shares does, in turn, help your search engine rankings, if only indirectly.
You not only need to have a strong social media presence yourself, but you also need to make it wicked easy to share your content and amplify those social signals.
10.) Real Business Information
This final tip is important for businesses targeting specific local geographic areas. The presence or absence of business information is one of the most critical local SEO ranking factors.
That being said, it’s important to look after areas like:
- NAP (name, address, and phone number)
- Business listings on Google My Business and Facebook
- Reviews on both Google My Business, Facebook, and relevant directories such as Yelp
- The most effective and accurate local search terms
That’s it! Now you have a working understanding of the essential SEO ranking factors.






